SQUEEZE
Title
SQUEEZE: Maximising Impact of Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Rheumatoid Arthritis with the Use of Biomarkers
SQUEEZE WP#8: Development, implementation and pilot testing of an innovative eHealth powered integrated care model for rheumatoid arthritis (work package leader)
Project Management
Sabina De Geest
Agnes Kocher
INS-Team
Sabina De Geest
Agnes Kocher
Janette Ribaut
Sofia Calado
Christina Wettengl
Doreen Siegels
External Partner
Medizinische Universität Wien, Österreich
Academisch Ziekenhuis Leiden, Netherlands
Diakonhjemmet Sykehus, Norway
Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
EUTEMA Research Services GmbH, Austria
Insituto de Salud Musculoesquelética, Spain
DAMAN, Denmark
Humanitas Mirasole, Italy
Oslo University Hospital, Norway
PrecisionLife, Denmark
European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR), Switzerland
Queen Mary University of London, United Kingdom
University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Carol Davila" Bucharest (Romania)
Location of Data Selection
Europe
Duration
2022 bis 2027
Description
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, immune-mediated and potentially disabling disease affecting approximately 5 million EU citizens, with a substantial personal and socioeconomic impact. The initiation of a (life-long) treatment with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is recommended directly after the diagnosis of RA. Whenever a patient does not reach remission, DMARD therapy should be adapted in the context of a shared decision making (SDM) process between the patient and healthcare provider.
However, it is currently not possible to predict which of the available DMARDs is the best choice for an individual patient. Without sufficient markers indicating the best choice for a particular patient, treatment strategies can be ineffective, cumbersome and expensive.
Moreover, current RA management strategies lack of care settings and digital tools that are permissive to full exploitation of drug benefits through SDM and adherence in the long run of a patient’s journey. Available patient-centred applications (Apps) for people living with RA do not reflect the cooperation of patients with their healthcare providers (i.e., SDM) regarding their wellbeing on a specific DMARD. While eHealth-supported integrated care models have been shown to improve adherence in chronically ill populations, such comprehensive care approaches are scarce for patients with RA and a clear unmet need.
For the development and implementation of a new care model, a good understanding of existing RA care processes and contextual factors –such as practice patterns of shared decision-making– is important to guarantee its real-world translation. The openness of patients and health professionals to technology must also be understood and taken into account in order to measure and improve behavioural and psychosocial well-being (e.g., medication adherence, medication side-effects, subjective symptom experience) via eHealth. Moreover, recent findings from other SQUEEZE work packages (e.g., therapeutic drug monitoring) and partners (e.g., eHealth strategies in RA) need to be considered when developing the care model.
Objectives
The SQUEEZE consortium has set out to maximise the impact of DMARDs in RA (by squeezing the most out of existing drugs) using clinical, laboratory, molecular, digital and behavioural biomarkers to:
- select the right DMARD for a specific patient at a specific point of his/her therapeutic journey;
- optimise the DMARD regimen (dose, route);
- inform an eHealth facilitated integrated care model.
Within the SQUEEZE consortium, the Basel project team is responsible for work package 8 (WP#8). Its overarching objective is to:
- develop, implement and pilot test theSQUEEZE eHealth facilitated integrated care model including digital therapeutics (SCM-DTx) focusing on patient´s preferences and needs to increase adherence to prescribed drugs.
Design / Methode
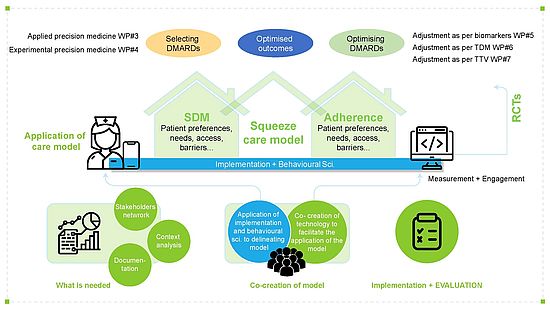
The overall conceptual approach of SQUEEZE is underpinned by a complementary methodological approach to address its objectives. SQUEEZE is committed to have a highly inter-professional interdisciplinary approach combining clinical and biological approaches in combination with behavioural and psychosocial digital approaches, implementation, and computer sciences, to address its objective. In total, the SQUEEZE work programme includes 9 thematically different work packages (WPs) that are supported by three pillars: (1) Selection of DMARDs; (2) optimising DMARDs; and (3) embedding the evidence from both into an innovative model of care (WP#8).
The SQUEEZE WP#8 project will be interlinked with the other SQUEEZE WPs. Using principles of chronic illness care and precision medicine, WP#8 will combine implementation, behavioural and agile computer science methods to ensure real-world translation. Together with our partners, we will use a step-wise approach to develop, implement and evaluate the SCM-DTx:
- Stakeholder involvement(Lead: INMUSC): An agile stakeholder involvement ecosystem will be developed using state-of-the-art stakeholder involvement methods to support the SCM-DTx development /evaluation as well as work of other WPs.
- Contextual analysis (Lead: UNIBAS): Using a multi-methods approach, variability in practice patterns of RA treatment (e.g., use of digital behavioural markers, DMARDs optimisation strategies, facilitators and barriers of chronic illness care) will be assessed across EU countries to map relevant practice/DTx factors supporting the subsequent development of the SCM-DTx.
- Co-creation of the SQUEEZE care model SCM-DTxwith end users (Lead: UNIBAS): Aiming at real-world translation, the development of the SCM-DTx will combine behavioural, implementation and computer science methods. The SCM-DTx will consist of intervention modules (e.g., behavioural digital biomarkers & PROs monitoring, medication adherence support, SDM; therapeutic drug monitoring, algorithms for drug match and dosage, etc.) and be delivered by human and digital mode (i.e., an optimised existing app). Implementation strategies to support real-world translation will also be co-created.
- Implementation and evaluation of the SQUEEZE care model SCM-DTx (Lead: UNIBAS): Using a hybrid effectiveness-implementation design (before-after design) the SCM-DTx will be implemented and pilot tested in 2 RA clinics. Effectiveness outcomes assessed will be digital behavioural markers (e.g., medication adherence), rates and satisfaction with shared decision making, rates of remission & low disease activity (LDA), impact of disease, as well as service (i.e., level of chronic illness care) and implementation outcomes (i.e., acceptability, appropriateness, feasibility, fidelity). A total of 150 adult RA patients per centre will be included (i.e., 75 pre implementation; 75 post implementation) as well as clinicians and relevant stakeholders for the evaluation of the implementation.
Expected Benefit / Relevance
The work programme proposed by the SQUEEZE consortium is a truly interrelated collaboration of leading centres in Europe that have come together for synergy and added value for addressing the objectives in a way that each one alone would not be able to. Within SQUEEZE WP#8, we will develop a novel eHealth-facilitated care model which includes personalised digital biomarkers to increase DMARDs effectiveness through optimized patient’s medication adherence and patient/clinician’s shared decision making. The participative and systematic approach has promising potential to improve the health outcomes of this population and – if proven effective – be a game changer in the lives of people with RA.

